
Top N3 Molecular Geometry Pics GM
21K views 3 years ago An explanation of the molecular geometry for the N3 - ion (Azide Ion) including a description of the N3 - bond angles. The electron geometry for the Azide Ion is.

N3 Lewis Structure How to Draw the Lewis Structure for N3 YouTube
481 149K views 10 years ago NO3- Lewis, Resonance, Shape, Formal Charges, and more. For the NO3- Lewis structure we can see that there are three Oxygen atoms around the central Nitrogen (N) atom..

Molecular Geometry of I3 TyrellanceHutchinson
Chemical Bonding: N 3 Lewis Structure Drawing the Lewis Structure for N 3- Viewing Notes: There are a total of 16 valence electrons in the N 3- Lewis structure. With N 3- you'll need to form two double bonds between the Nitrogen atoms to fill the octets and still use only the 34 valence electrons available for the molecule.

AsF3 Molecular Geometry Science Education and Tutorials
Written by Priyanka in Lewis Structure The chemical formula N3- represents the Azide ion. The Azide ion is a conjugate base of Hydrazoic acid (HN3). It is composed of three Nitrogen atoms and can have multiple resonance structures.

Answered Give the electrondomain and molecular… bartleby
Azide [N3]- ion Lewis structure, molecular geometry or shape, resonance structure, polar or non-polar, hybridization, bond angle N 3- is the chemical formula for the azide ion, also known as hydrazoate. It is an anion composed of three nitrogen (N) atoms. It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid/ hydrogen azide (HN 3 ).
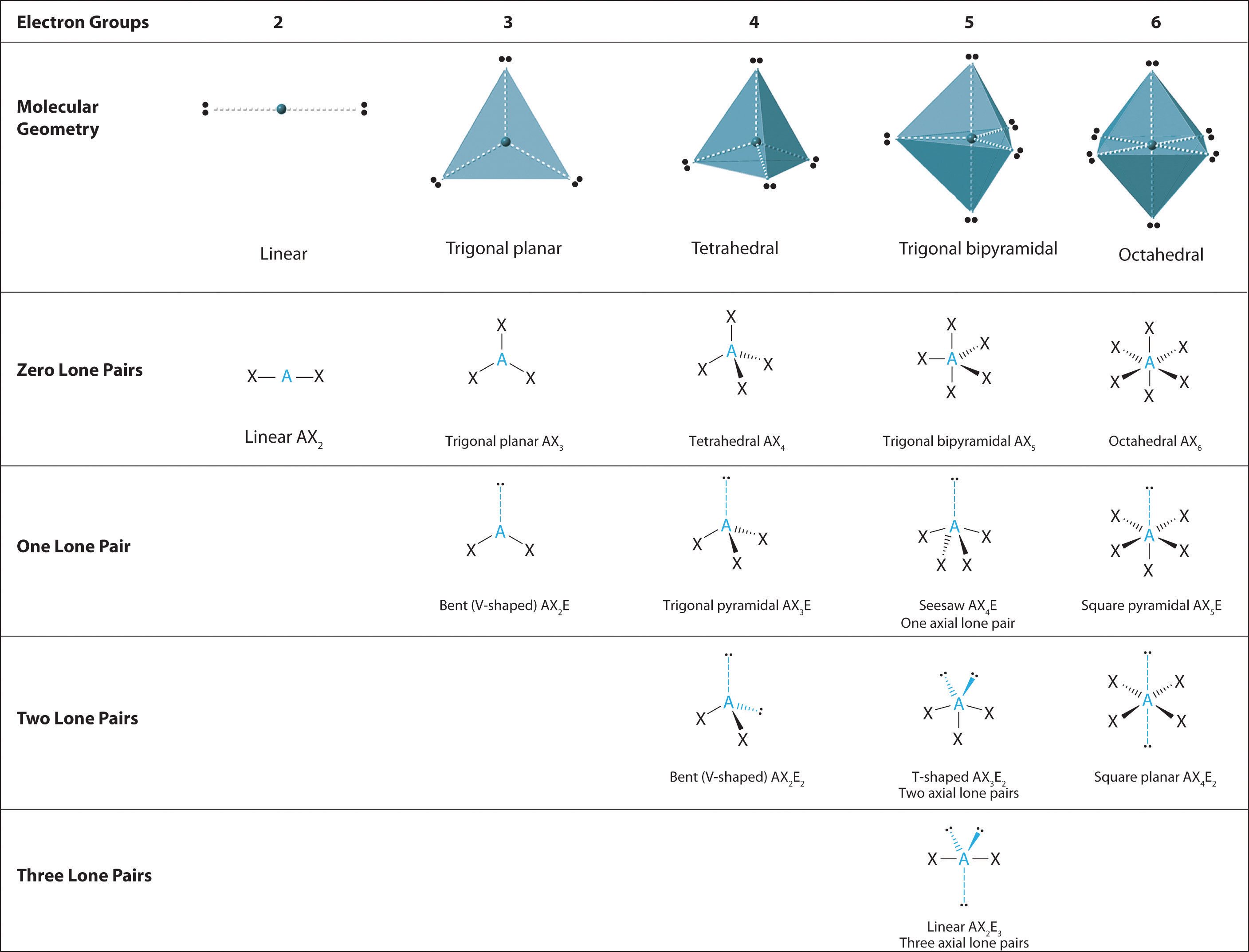
1.3 VSPER Theory The Effect of Lone Pairs Chemistry LibreTexts
1. N3- Lewis Structure: Here's a step-by-step guide on drawing the N3 - Lewis structure. Step 1: draw sketch • To begin, count the total amount of valence electrons. Nitrogen is in group 15 of the periodic table. As a result of this, nitrogen has five valence electrons. Because N 3- contains three nitrogen atoms,

The electron pair geometry and shape around C2 and N3 in the molecule
Describe the molecular geometry of N 3 −. Molecular geometry: There are five electron-pair geometries: linear, trigonal planar, octahedral, tetrahedral, and trigonal bipyramidal.

11333.jpg
The molecular geometry about each N is trigonal pyramidal. The number of hybrid orbitals used by the central atom is the same as the number of electron pairs around the central atom. Hybridization Using d Orbitals. Hybridization is not restricted to the ns and np atomic orbitals. The bonding in compounds with central atoms in the period 3 and.

Is NO3 Polar or Nonpolar? Techiescientist
tetrahedral shape. If these are all bond pairs the molecular geometry is tetrahedral (e.g. CH 4). If there is one lone pair of electrons and three bond pairs the resulting molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal (e.g. NH 3). If there are two bond pairs and two lone pairs of electrons the molecular geometry is angular or bent (e.g. H 2O).

Lone Pair of Electrons
Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers 4. Using the Lewis dot structure, predict the molecular geometry of the following and state the hybridization and bond angle of the central atom. a. N3- b. NO3- c. BF4- d. CH4 e. C2H2 This problem has been solved!
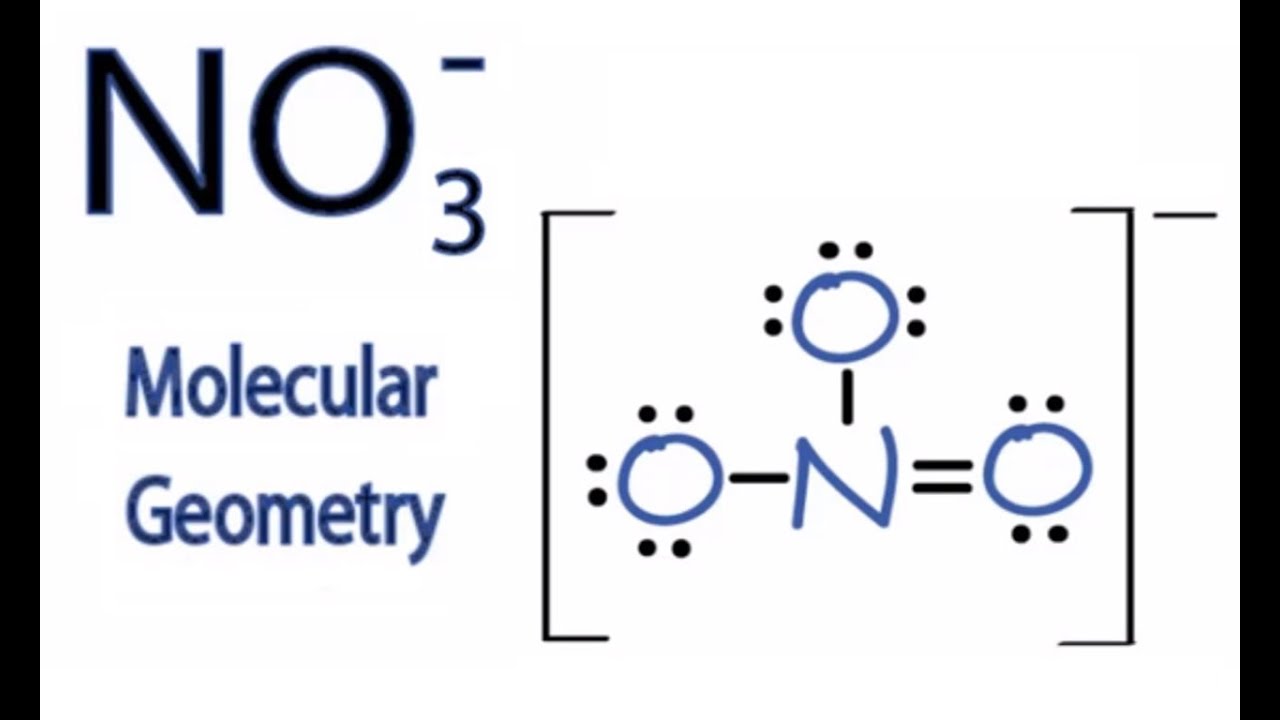
NO3 Molecular Geometry / Shape and Bond Angles YouTube
Geometry of Molecules. Molecular geometry, also known as the molecular structure, is the three-dimensional structure or arrangement of atoms in a molecule. Understanding the molecular structure of a compound can help determine the polarity, reactivity, phase of matter, color, magnetism, as well as the biological activity.

Nitride Ion
Azide. The azide anion. In chemistry, azide ( / ˈeɪzaɪd /, AY-zyd) is a linear, polyatomic anion with the formula N− 3 and structure −N=N+=N−. It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid HN3. Organic azides are organic compounds with the formula RN3, containing the azide functional group. [1] The dominant application of azides is as a.

Consider the molecule below. Determine th... Physical Chemistry
D With two nuclei around the central atom and one lone pair of electrons, the molecular geometry of SnCl 2 is bent, like SO 2, but with a Cl-Sn-Cl bond angle of 95°. The molecular geometry can be described as a trigonal planar arrangement with one vertex missing. Exercise. Predict the molecular geometry of each molecule. SO 3; XeF 4.

Hybridization, Molecular Geometry and Bond Angles without/with lone
In the N 3- Lewis structure, there are two double bonds around the nitrogen atom, with two other nitrogen atoms attached to it, and on the left and right nitrogen atoms, there are two lone pairs. Also, there is a negative (-1) charge on the left and right nitrogen atoms, and a positive (+1) charge on the center nitrogen atom.
Solved Make molecular models of the compounds listed in the
In the Lewis Structure for N3- you'll need to place a double bonds between the Nitrogen atoms to achieve full outer shells on all atoms while only using the valence electrons available for the molecule. For the N3- Lewis structure, calculate the total number of valence electrons for the N3- molecule.

N3 (Azide Ion) Molecular Geometry, Bond Angles & Electron Geometry
I quickly take you through how to draw the Lewis Structure of N3- (Azide Ion) . I also go over hybridization, shape and bond angles.